A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. The mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, grinding grain, pumping water etc.
Recommended Project: Hybrid Compressed Air Energy Storage (HCAES) Systems Renewable Energy
The device is called a windmill or wind pump. Developed for over a millennium, today's wind turbines are manufactured in a range of vertical and horizontal axis types. The smallest turbines are used for applications such as battery charging or auxiliary power on sailing boats; while large grid-connected arrays of turbines are becoming an increasingly large source of commercial electric power.
Wind power technology is the various infrastructure and process that promote the harnessing of wind generation for mechanical power and electricity. This basically entails the wind and characteristics related to its strength and direction, as well as the functioning of both internal and external components of a wind turbine with respect to wind behavior.
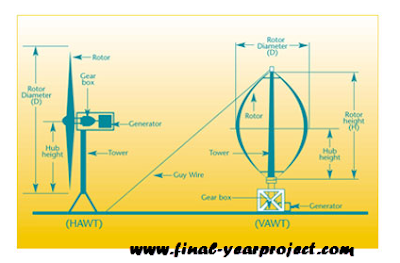
Vertical-axis wind turbines (or VAWTs) have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically. Key advantages of this arrangement are that the turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind to be effective. This is an advantage on sites where the wind direction is highly variable, for example when integrated into buildings.
There are also few subtypes of VAWT viz. Darrieus wind turbine, Savonius wind turbine, Giromill. Since VAWTs are easy to maintain, and can be installed near ground level, they are preferred over HAWTs when it comes to home use. This way, private home owners wouldn’t have to spend a lot of resources to get the wind turbine to work if compared with installing a HAWT.
Author:- Indramani singh vishal
Download
Advertisements:-








No comments:
Post a Comment